Lipid droplet (LD) is the major organelle governing lipid storage such as triacylglycerol (TAG). LDs universally exist in many prokaryotic and almost all eukaryotic cells. LD function disorders are closely related to metabolic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease. Most organelles consist of double layer phospholipids. Liposomes, which are formed by phospholipids in aqueous solution, are also composed of lipid bilayer and utilized to resemble the double-layer-phospholipid-bound organelles in vitro. However, LDs have unique structures with monolayer phospholipid covering neutral lipid core, which makes it impossible to use liposome for in vitro LD study. In the study, entitled Construction of Nano-Droplet/Adiposome and Artificial Lipid Droplets, which was published online on Feb. 24, 2016 in ACS Nano, Prof. LIU Pingsheng’s group develops a new system to construct and purify nano-particles that consist of monolayer phospholipids and neutral lipid core, which resembles the structure of LDs without proteins. They termed this structure “adiposome”, in analogy to the “liposome”. In the study, Prof. LIU’s lab also constructed artificial lipid droplets (ALDs) by recruiting prokaryotic and eukaryotic LD resident/structure-like and functional proteins on adiposomes. The construction system of adiposome and ALD will promote the development of LD study by providing new method for the research of LD protein function and the interaction with other organelles. Lipoproteins in blood have similar structures with LDs. In the study, LIU’s group also successfully obtained artificial lipoproteins by recruiting Apo A-I, the major protein in HDL, to adiposomes. The artificial lipoproteins only consist of biological materials and thus are degradable and biocompatible. The neutral lipid core may contain a mass of hydrophobic medicines. Thus, the adiposomes and artificial lipoproteins are very promising potential nano drug delivery carriers. 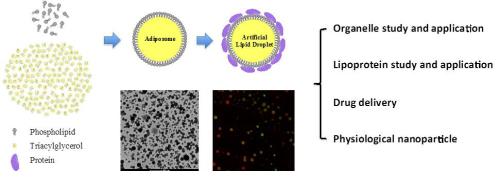
Figure legend: The Scheme of adiposome and artificial lipid droplet construction (Image by IBP) The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China. Article link: CONTACT: Pingsheng Liu National Laboratory of Macrobiomolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing 100101, China Phone: 86-10-64888517 Email: pliu@ibp.ac.cn |