Zusen Fan lab reveals a new molecular mechanism on self-renewal of liver cancer stem cell
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common liver cancer, is the third leading cause of cancer related death. A subset of cells with stem/progenitor cell features known as cancer stem cells (CSCs), accounting for tumor initiation, metastasis, drug resistance and recurrence, emerge as a potential target for tumor eradication. However, the molecular mechanisms to sustain liver CSCs remain largely unknown.
To search for driver genes in the oncogenesis of HCC and self-renewal maintenance of liver CSCs, researchers from Zusen Fan lab at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences performed genome-wide analyses using several online-available HCC transcriptome datasets. They found C8orf4 was weakly expressed in liver cancer cells, liver stem cells and liver CSCs. Sphere formation and xenograft formation confirmed that C8orf4 inhibitsthe self-renewal of liver CSCs. Moreover, C8orf4 interacts with Notch2 intracellular domain (N2ICD), blocks its nuclear translocation, and finally inhibits Notch signaling. Importantly, Notch2 signaling activation is well correlated with severity and prognosis of HCC patients. Thus, targeting Notch2 signaling might be used to eradicate liver CSCs for future therapy.
This study was published online on May 19, 2015 in Nature Communications entitled “C8orf4 negatively regulates self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells via suppression of NOTCH2 signaling”.
Zusen Fan is the corresponding author.Pingping Zhu, a Ph.D candidate, is the first author. Yanying Wang, Ying Du, Lei He, Guanling Huang, Geng Zhang and Xinlong Yan performed experiments in this study. Dr. Lei He was also contributed to this study.
This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
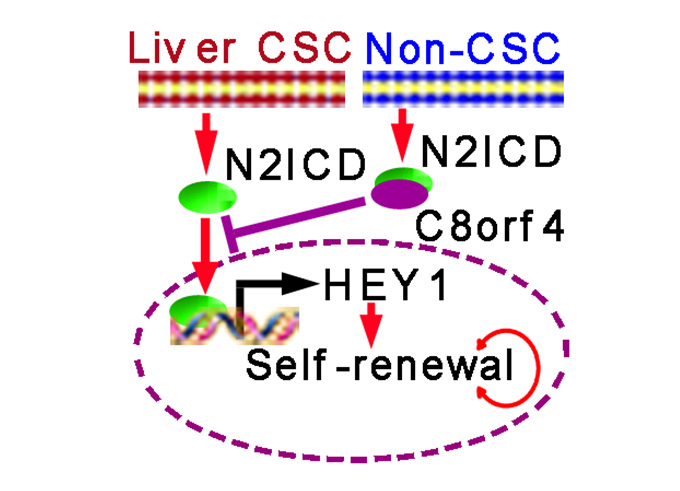
Legend: A working model on the regulation of Liver CSC self-renewal by C8orf4. (image by IBP)
Contact:
Zusen Fan, The CAS key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China,E-mail: fanz@moon.ibp.ac.cn

