IBP Scientists Elucidated Generation and Loading of DNA Guides by Bacterial Argonaute
Argonaute (Ago) proteins are key components of eukaryotic RNAi pathways. Eukaryotic Ago proteins utilize small RNA guides to target complementary RNA molecules. The small RNA guides are processed and loaded by Dicer and other proteins. In contrast, several prokaryotic Ago proteins utilize small DNA guides to mediate host defense by targeting invading DNA complementary to the DNA guide. It remains elusive how the small interfering DNA (siDNAs) guides are generated and loaded onto Ago proteins.
Thermus thermophiles Ago (TtAgo) interferes with plasmid transformation guided by siDNA. These siDNA guides are 5'phorylated and are 13–25 nt in length. Most of the TtAgo-bound siDNAs have a deoxycytidine at the 5'end, suggesting a specific mechanism for guide generation and/or guide loading.
On 2nd March, 2017, Prof. WANG Yanli’s lab in IBP and collaborators from Netherlands published a paper entitled Autonomous Generation and Loading of DNA Guides by Bacterial Argonaute.
In this study, WANG Yanli’s lab in IBP and collaborators from Netherlands demonstrated that TtAgo can independently generate and selectively load functional DNA guides. They found that the guide-free TtAgo is able to degrade unstable double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) targets, generating short DNA products, which are selectively loaded onto TtAgo and guide subsequent DNA target cleavage. They also showed that TtAgo loads dsDNA molecules with a preference toward a deoxyguanosine on the passenger strand at the position opposite to the 5′ end of the guide strand. This explains why in vivo TtAgo is preferentially loaded with guides with a 5′ end deoxycytidine.
This research was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The X-ray diffraction data were collected at the BL-17U1beamline at SSRF.
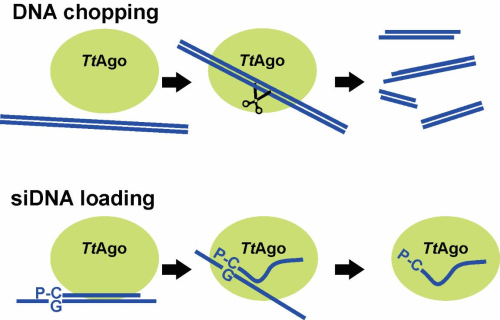
Figure 1. Generation and loading of DNA guides by TtAgo protein (Image by Wageningen University)
Contact:
WANG Yanli
Principal Investigator
Institute of Biophysic, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: ylwang@ibp.ac.cn
Tel:86-10-64881316

