Nanocage-based Capture-Detection System for the Clinical Diagnosis of Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune diseases are induced by the loss of immune tolerance to autoantigens, thus producing autoantibodies and resulting in histopathological diseases. The detection of autoantibodies is critical for the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases. However, the sensitivity is often limited by the properties of the antigens and the detection systems such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Here, by employing the multidisplay ability of ferritin, a highly sensitive nanocage-based capture-detection system is designed, of which the sensitivity is 100-1000-fold higher than that of conventional ELISA methods. On May 24, 2021, the results were published in the journal of Small as a frontispiece.
The polymer-antigen is constructed by displaying the primary Sjogren's syndrome (pSS)-related antigenic peptides on ferritin nanocage, which is capable of presenting epitopes effectively and with high affinity, leading to tenfold higher capture capability for autoantibodies. Human IgG Fc-binding peptides are also engineered on ferritin nanocage, which enable high binding affinity and efficient horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeling. Compared to commercial HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG antibody, polymer-antigen exhibited more than ten-fold increase in the sensitivity. Employing this nanocage-based capture-detection system for the detection of autoantibodies, we found that it is 100-1000-fold more sensitive than that of conventional ELISA methods. 91 sera from patients with pSS, 51 from rheumatoid arthritis, 54 from systemic lupus erythematosus, and 55 from healthy individuals were analyzed by using the nanocage-based ELISA. The results showed that the nanocage-based capture-detection system significantly improved the detection sensitivity and positive rates when compared with that of the conventional ELISA system. These results indicate that the nanocage-based capture-detection system is an effective detection platform and provide a novel and more sensitive method for the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases.
Prof. FAN Kelong, Prof. YAN Xiyun from the Institute of Biophysics and Prof. LI Zhanguo from the Peking University People's Hospital are the co-corresponding authors of this paper. ZHANG Yanan from the Institute of Biophysics and LI Yingni from the Peking University People's Hospital contributed equally as the first authors. The research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, CAS Interdisciplinary Innovation Team, Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (CAS), National Key Research and Development Program of China and Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
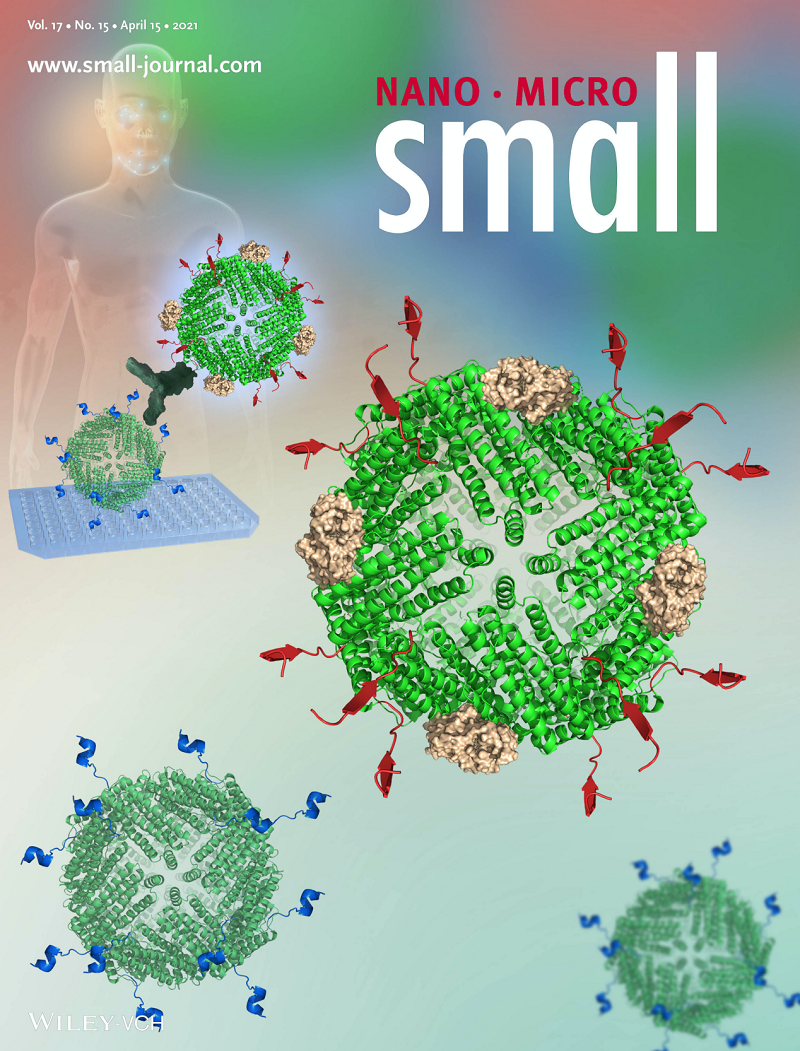
Nanocage-Based Capture-Detection System for the Clinical Diagnosis of Autoimmune Disease
Fulltext link:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.202101655
Contact: FAN Kelong
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing 100101, China
Email: fankelong@ibp.ac.cn
(Reported by Dr. YAN Xiyun's group)

