Diagnostic value of salivary real-time quaking-induced conversion in Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy
Aggregation of α-synuclein (oligomeric α-syn) has been considered as the pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease (PD) and multiple system atrophy (MSA), although the discrimination of these two types of synucleinopathies is difficult. Previous studies have successfully applied real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) assay to detect the seeding activity of α-syn in various biological samples for the diagnosis of PD or MSA, such as brain, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), skin and olfactory mucosa samples. However, there is a lack of non-invasive and easily accessible biological samples for RT-QuIC reaction in the diagnosis of synucleinopathies.
In this study, a total of 75 patients with PD, 18 patients with MSA, and 36 non-neurodegenerative normal controls (NNCs) underwent salivary α-syn real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) assay. Overall, salivary α-syn RT-QuIC assay distinguished PD patients with 76.0% sensitivity (95% CI, 66.1-85.9) and 94.4% specificity (95% CI, 86.6-100.0) from controls. RT-QuIC assay sensitivity reached 61.1% (95% CI, 36.2.1-86.1) in MSA patients. Notably, the lag phase of RT-QuIC assay from PD patients was significantly shorter than that of MSA patients, which might be clinically applicable to the discrimination between PD and MSA. These results reveal saliva as a non-invasive and easily accessible biospecimen for α-syn detection by RT-QuIC assay in the diagnosis of PD and MSA.
This study entitled " Diagnostic value of salivary real-time quaking-induced conversion in Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy " was published on-line in the journal Movement Disorders on 12 March 2022. Dr. ZHU Li from the Institute of Biophysics Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Drs DENG Jianwen and WANG Zhaoxia from Peking University First Hospital are the corresponding authors. The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research and Development Program, Peking University and State Key Laboratory of Brain and Cognitive Science.
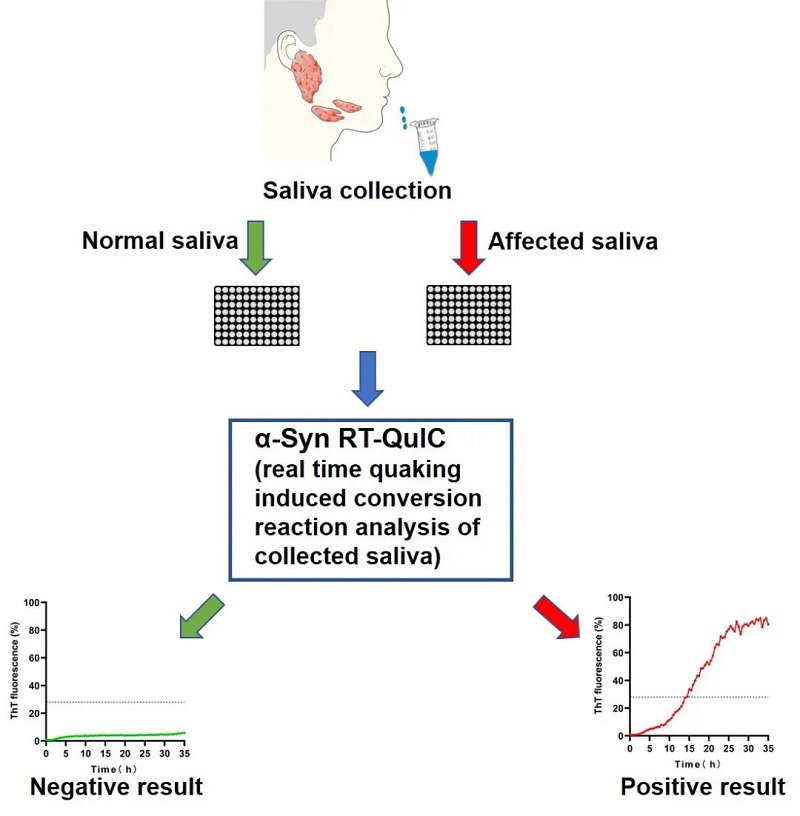
Figure 1. Salivary RT-QuIC assay to detect the seeding activity of α-syn.
Article link:
https://movementdisorders.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mds.28976
CONTACT: ZHU Li
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing 100101, China
Phone: 86-10-64888303
Email: zhuli@ibp.ac.cn
(Reported by Molecular Neurobiology group)

