The group of Prof. BU Pengcheng and collaborators revealed that CLMP determines all-trans retinoic acid response in colorectal cancer
On Nov 8, 2023, Developmental Cell published a research article by researchers lead by Prof. BU Pengcheng at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Prof. LIU Jinbo at the 1st affiliated hospital of Zhengzhou University and Prof. ZHANG Peng at Capital Medical University, National Center for Children's Health. The paper by Wu and Zhang et al. entitled “CLMP is a tumor suppressor that determines all-trans retinoic acid response in colorectal cancer” reveals that CLMP is a tumor suppressor and determines all-trans retinoic acid response in colorectal cancer (CRC).
All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), the major biological active metabolite of vitamin A, has shown substantial effect for the treatment of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia, and also been under an increasing number of clinical trials against various types of cancer, including melanoma, neuroblastoma and pancreatic cancer. However, the effect of ATRA is controversial on CRC, as some CRC respond to ATRA, some do not, while the mechanism that regulates the response of ATRA on CRC remains to be elucidated.
CAR-like membrane protein (CLMP), is dramatically overexpressed in intestine. CLMP mutations were observed in intestine, resulting in congenital short-bowel syndrome (CSBS), a disease with high mortality, indicating that CLMP plays a critical role in intestinal development. However, its functions in CRC remain elucidated.
The researchers analyzed the expression of CLMP in CRC tissues in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The results showed that CLMP is downregulated in CRC, and associated to CRC progression. Then researchers generated Clmp conditional knockout mice in intestinal epithelial cells. Loss of CLMP enhanced intestinal carcinogenesis in both AOM/DSS and ApcMin/+ mouse models.
To reveal the molecular mechanism how the CLMP regulates tumorigenesis and growth of CRC, researchers examined proteins interacting with CLMP by co-immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry. CLMP interacted with β-catenin, recruiting β-catenin to cell membrane and suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cytochrome P450 hydroxylase A1 (CYP26A1) was found to be targeted by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and significantly upregulated in Clmp null tumors via RNA Seq. CYP26A1 is the key enzyme that degrades retinoic acid into less bio-active retinoid. CLMP knockdown increased CYP26A1 expression in CRC57 cells and resulted in the cells resistant to ATRA. Notably, the cells became sensitive to ATRA when CYP26A1 was knocked down, demonstrating that CYP26A1 was required to CLMP knockdown-mediated cell proliferation. Furthermore, CLMP expression is negatively associated with nuclear β-catenin and CYP26A1 expression in clinical CRC samples. In addition, combination of ATRA and CYP26A1 inhibitor suppressed CLMP downregulation-mediated CRC tumorigenesis and growth in ApcMin/+, AOM/DSS and orthotopic CRC mouse models.
Putting together, researchers identify the anti-CRC role of CLMP and suggest that CYP26A1 inhibitor enable to boost ATRA’s therapeutic efficiency.
Prof. BU Pengcheng at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Prof. LIU Jinbo at the 1st affiliated hospital of Zhengzhou University and Prof. ZHANG Peng at Capital Medical University are co-correspondent authors of this paper. WU Zhenzhen, an assistant researcher, and ZHANG Xuanxuan, a Ph.D. student, are the co-first authors of this article. This research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the CAS, CAS project for young scientists in basic research, the NSFS Innovative Research Group Foundation, and grant from the Beijing Natural Science Foundation of China.
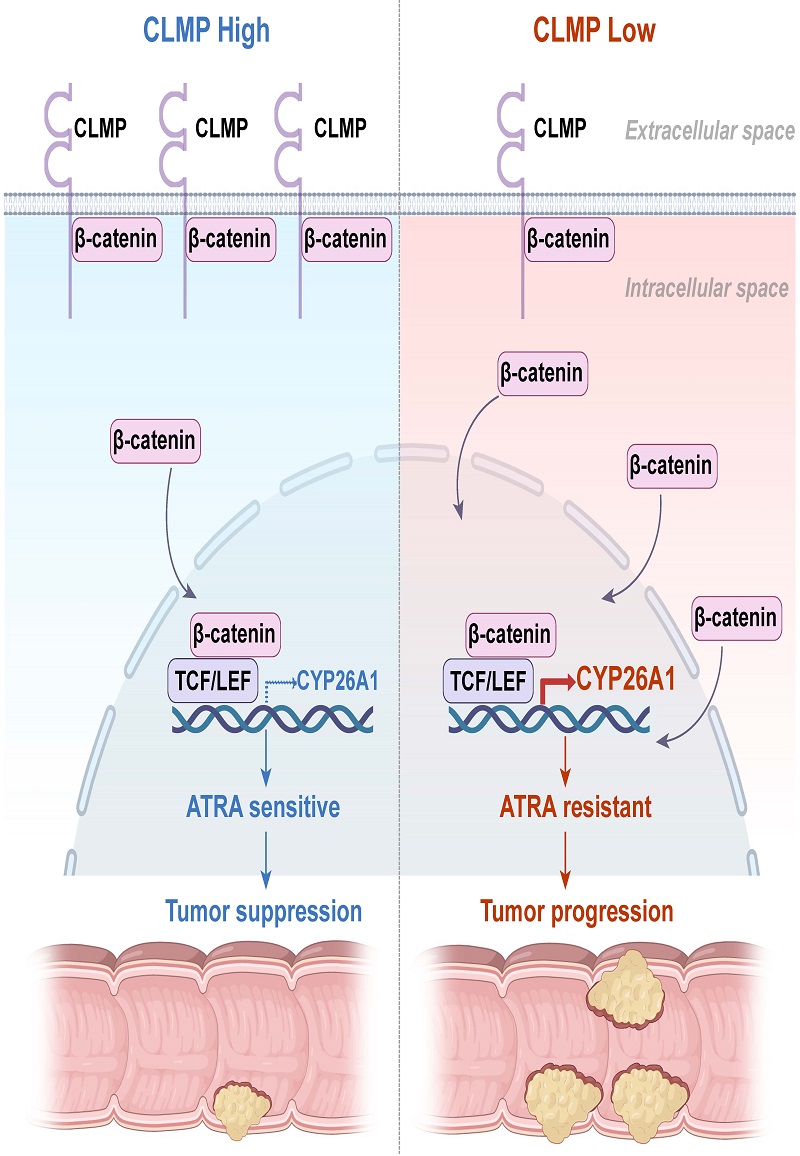
Figure 1. CLMP regulates ATRA response via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in CRC
Article link: https://www.cell.com/developmental-cell/fulltext/S1534-5807(23)00525-7
Contact: BU Pengcheng
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing 100101, China
Email: bupc@ibp.ac.cn
(Reported by Prof. BU Pengcheng’s group)

