A novel peptidomic strategy based on single-position peptide clustering
In the field of omics research, peptidomics occupies a unique position and is highly complementary to proteomics, though its development has lagged relatively. For a long time, peptidomics has faced a core dilemma: how to accurately capture disease-related "fingerprint" features from thousands of apparently chaotic peptide fragments.
On November 18, 2025, a research article entitled "Single-Position Peptide Clustering for Peptidomics Reveals Novel Disease Biomarkers and Dysregulated Proteolytic Characteristics" was published in Advanced Science, by YANG Fuquan's group from the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with collaborators GUO Xiangqian from Henan University. A novel "amino acid score" (aa-score) algorithm and single-position peptide clustering based strategy was has been proposed for peptidomics.
The innovation of this research strategy lies in introducing the core algorithm of "amino acid score" (aa-score) based on the complexity of peptides produced by protein proteolysis and the specificity of cleavage sites.
Rather than treating each peptide in isolation, the strategy comprehensively quantifies and scores all redundant peptides derived from the same protein with the same characteristic amino acid site. It systematically integrates the diversity of proteolytic peptides into single-position peptide clusters and evaluates these clusters as holistic functional units. At the same time, the strategy directly links substrates, specific protease activities, and their pathophysiological implications in disease, providing an analytically more biologically interpretable framework. This achieves theoretical innovation in the analytical approach to disease-related peptidomics data.
The researchers also proposed a new concept of "amino acid position-based peptide cluster biomarkers," successfully transforming large amounts of seemingly chaotic peptide information into clear "diagnostic codes."
In clinical application studies on β-thalassemia, the researchers not only identified novel peptide cluster biomarkers but also gained profound mechanistic insights into processes such as the dysregulated proteolysis of AHSG protein.
This work brings a fresh perspective to the field of peptidomics and is expected to drive further advances in disease diagnosis and therapeutic development.
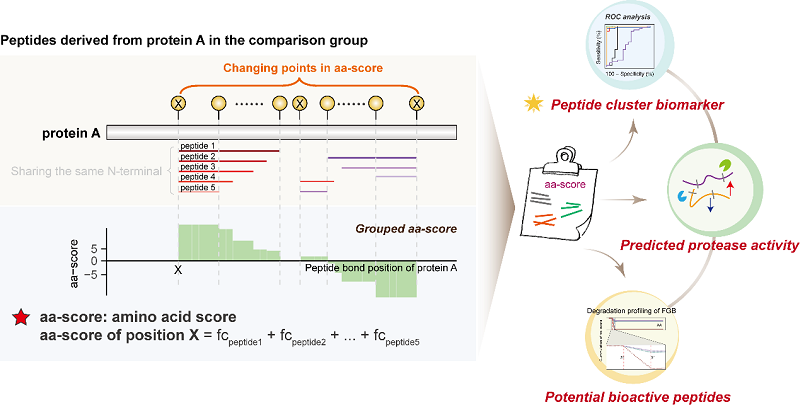
Figure: A novel peptidomic strategy based on single-position peptide clustering
(Image by YANG Fuquan's group)
Article link: https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202510910
Contact: YANG Fuquan
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing 100101, China
E-mail: fqyang@ibp.ac.cn
(Reported by Prof. YANG Fuquan's group)

