Structural analysis indicates Orc6 protein’s role in DNA replication
DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms. It is the basis for biological reproduction and inheritance. The Origin Recognition Complex (ORC) is a six-subunit protein complex important for the initiation of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. It recognizes and binds DNA origin for eukaryotic replication. Orc6 is the smallest subunit in the complex and was known to be required for both DNA replication and cytokinesis. However, the function of Orc6 is not clear.
In a recent study, Dr. Yingfang Liu, Professor of the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and his colleagues determined the structure of human Orc6 middle region (Orc6-M), which includes amino acids 94–187. This domain has an overall fold similar to the corresponding helical domain of transcription factor TFIIB. Based on these findings, they produced a model of Orc6 binding to DNA. They identified amino acids of Orc6 which are directly involved in DNA binding. Alterations of these amino acids abolish DNA binding ability of Orc6 and also result in reduced levels of DNA replication in vitro and in cultured cells. Their data indicate that Orc6 is one of the DNA binding subunits of ORC in metazoan species. They propose that Orc6 may participate in positioning of ORC at the origins of DNA replication similar to the role of TFIIB in positioning transcription preinitiation complex at the promoter.
This work was conducted collaborating with Professor Igor Chesnokov, University of Alabama, USA and published online on April 18, 2011 by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal as an original research paper titled “Structural analysis of human Orc6 protein reveals a homology with transcription factor TFIIB”.
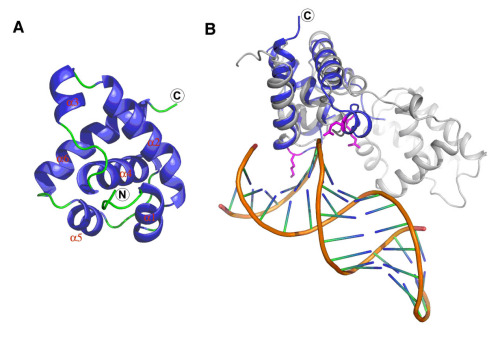
Figure. Structure of human Orc6. (A) Structure of human Orc6 helical domain; (B)Superimpose of Orc6 to TFIIB-DNA complex. Orc6 helical domain is shown in color blue, TFIIB is shown in grey and double-stranded DNA is color in gold. The three residues, K168, Q129 and R137 of Orc6, that are involved in DNA binding are shown in magenta. (by Shixuan Liu, et al)
(By Lingfei Kong)

