The P5A type ATPase/CATP-8 safeguards ER identity by clearing ectopic localized proteins
Stringent targeting of membrane proteins to their corresponding organelles is essential for organelle identity and physiological functions. Membrane protein localization requires not only high fidelity protein targeting but also quality control system to selectively remove mistargeted proteins. Although the conserved AAA-ATPase Msp1 clears mistargeted proteins from the outer membrane of mitochondria (OMM), the surveillance mechanism which removes mistargeted proteins from ER is still unknown.
Recently, Researchers from Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (QIN Qing and Dr. WANG Xiangming) and Stanford University (Prof. SHEN Kang) published a paper entitled "An endoplasmic reticulum ATPase safeguards ER identity by removing ectopically localized mitochondrial proteins" in Cell Reports. It reported a function of the ER protein P5A ATPase/CATP-8, the worm homolog of ATP13A1 (mammalian) and Spf1 (yeast), as a surveillance mechanism to remove mistargeted mitochondrial SA/TA proteins from ER membrane.
Multiple mitochondrial SA/TA proteins were mistargeted to ER in catp-8 mutants. While two transmembrane mitochondrial protein FZO-1 was not influenced. CATP-8 localized to ER which suggests that CATP-8 functions on ER. Interestingly, by photoconversion and heatshock experiment, it showed that CATP-8 could remove mistargeted mitochondria proteins from ER, which was independent of ERAD pathway. Furtermore, the mitochondrial fission factors FIS-1 and MFF-2 were mistargeted to ER in catp-8 mutant. The mistargeting of mitochondrial fission factors caused ectopic recruitment of mitochondrial fission protein DRP-1 to ER, which induced ER fragmentation. CATP-8 was essential for PVD neuron dendrite morphogenesis by controlling the level of dendritic receptor DMA-1.
This study uncovered a novel role for the conserved ER protein P5A ATPase/CATP-8 as a surveillance role on ER membrane to clear ectopic mitochondrial TA/SA proteins, and its significance in maintaining the ER identity and normal function.
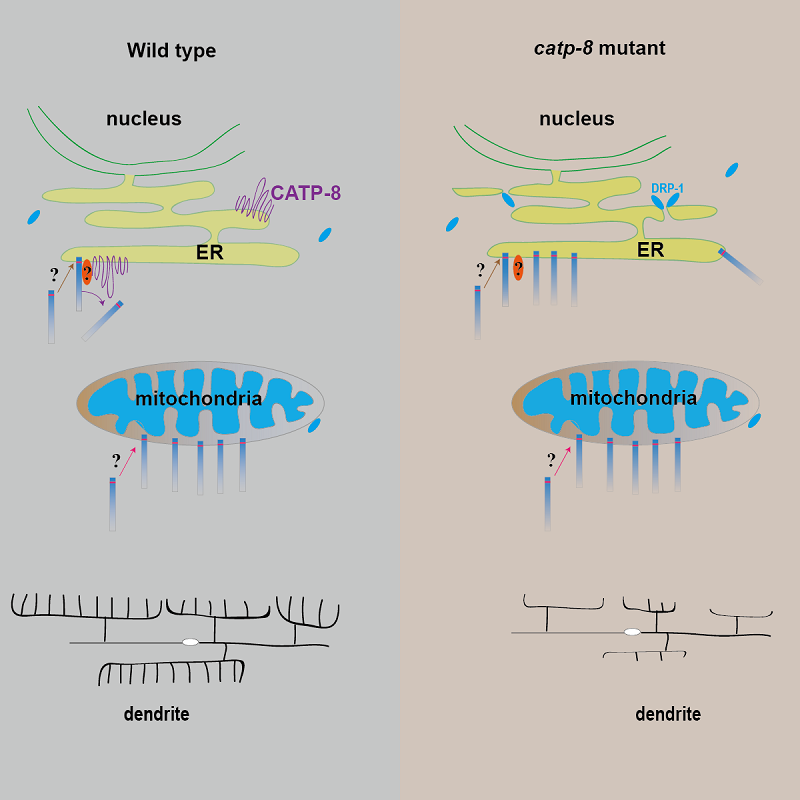
The P5A type ATPase/CATP-8 safeguards ER identity by clearing ectopic localized proteins
(Image by Dr. WNAG Xiangming's group)
The web link of this paper: https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(20)31352-8
Contact: WANG Xiangming
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing 100101, China
Email: xmwang@ibp.ac.cn
(Reported by Dr. XU Tao's group)

