SARS-CoV-2 RNA Interacts with and Stabilizes Host mRNAs to Elicit Cytokine Storm
SARS-CoV-2 is the pathogen of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). SARS-CoV-2 infection can suppress interferon (IFN) response and simultaneously induce the production of various cytokines, which directly trigger cytokine storm, a leading cause of death in COVID-19 patients. However, how SARS-CoV-2 elicits cytokine storm remains elusive.
Xue Yuanchao's team and their collaborators globally profiled the SARS-CoV-2-to-host RNA-RNA interactions to address this question. They unexpectedly found that SARS-CoV-2 RNA can interact with and stabilize host mRNAs to elicit cytokine storm. This study was published online in Molecular Cell on Dec. 20.
Researchers used a state-of-the-art RIC-seq technology to comprehensively map the SARS-CoV-2 and host RNA-RNA interactions in infected cells and lung tissues from two dead COVID-19 patients. They found that SARS-CoV-2 RNA can form 2,095 potential duplexes with the 3' UTRs of 205 host mRNAs to increase their stability by recruiting RNA-binding protein YBX3 in A549 cells. Disrupting the SARS-CoV-2-to-host RNA duplex or knocking down YBX3 reduced host mRNA stability and viral replication.
Among SARS-CoV-2-stabilized host targets, NFKBIZ appears crucial for promoting cytokine production and simultaneously reducing interferon responses, probably contributing to cytokine storm induction. Upon NFKBIZ knockdown, the expression levels of proinflammatory factors such as IL6, IL8, and CXCL2 were decreased significantly, whereas type I/III IFNs, IFNB1, IFNL1, and IFNL2 were increased. These results suggest that SARS-CoV-2 may induce cytokine storm via stabilized host mRNAs, especially NFKBIZ.
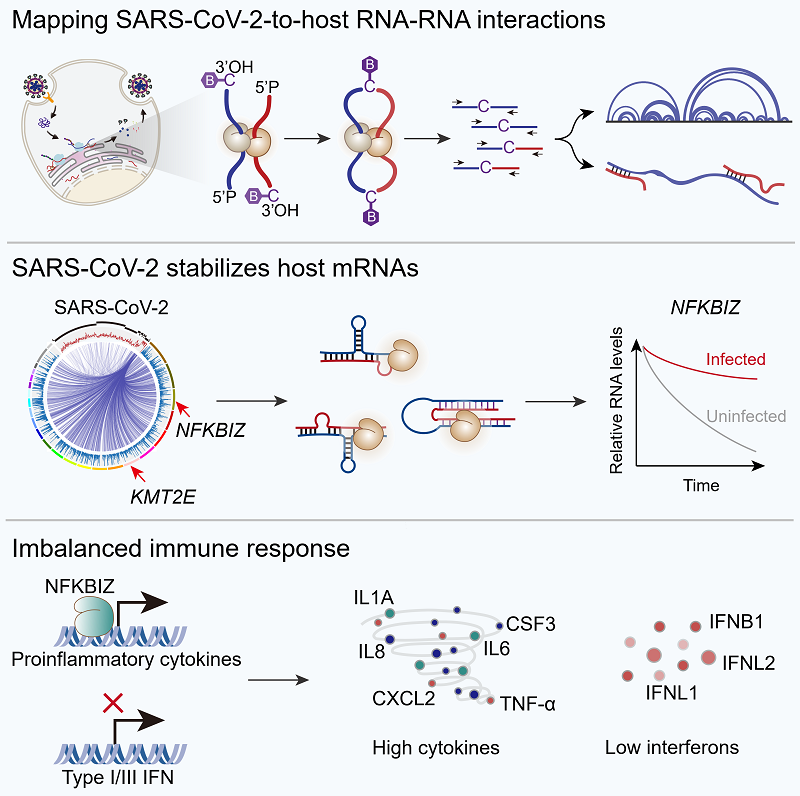
Figure:SARS-CoV-2 stabilizes host mRNAs to induce cytokine storm
This research uncovers the crucial roles of RNA-RNA interactions in the immunopathogenesis of RNA viruses like SARS-CoV-2 and provides valuable host targets for drug development.
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2023.11.032
Contact: XUE Yuanchao
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing 100101, China
Email: ycxue@ibp.ac.cn
(Reported by Dr. XUE Yuanchao's group)

