Scientists Build a Spatiotemporal Multi-omics Database for Human and Non-human Primate Brains: MAPbrain
In recent years, with the rapid advancement of neurodevelopmental research and high-throughput technologies such as single-cell sequencing, spatial transcriptomics, and single-cell epigenomics, a vast amount of multi-omics data related to brain development has emerged. However, there is still a lack of a comprehensive resource dedicated to integrating these brain development-related multi-omics datasets, limiting researchers' ability to fully uncover the brain's developmental processes and influencing factors from multiple dimensions.
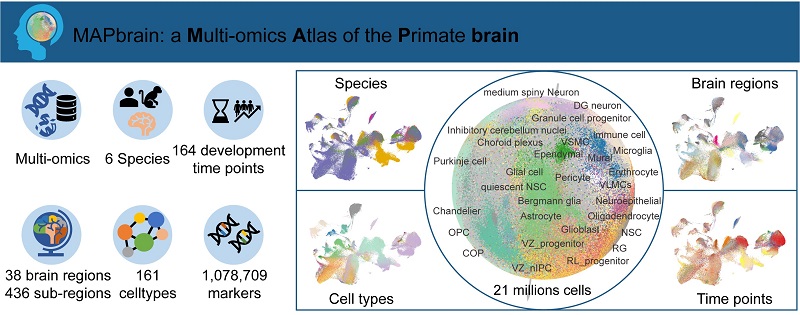
A research team from the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Beijing Normal University has integrated datasets related to brain development from different layers, including single-cell transcriptomics, spatial transcriptomics, and epigenomics, to build the MAPbrain, a Multi-omics Atlas of the Primate brain.
This is the first database focusing on the collection and integration of multi-omics data related to primate brain development, revealing the spatiotemporal dynamics of gene expression regulation during brain maturation. (http://bigdata.ibp.ac.cn/mapBRAIN/)
This study was published in Nucleic Acids Research on October 18, 2024.
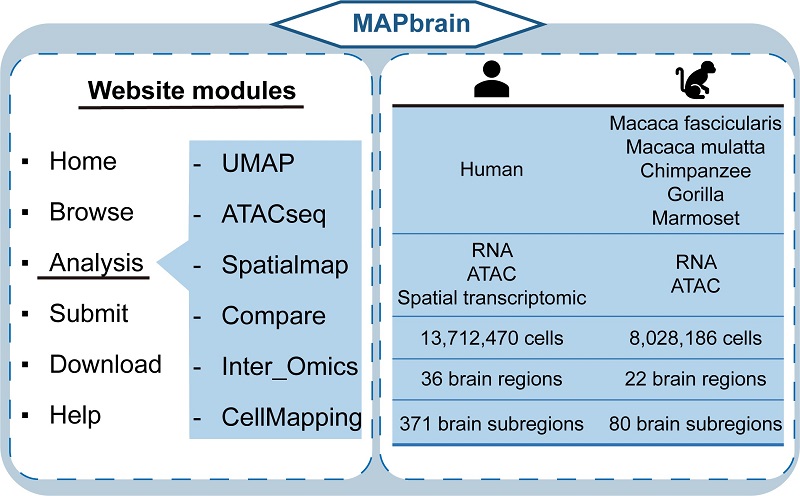
The database integrates three types of omics data from humans and five non-human primate species, covering six species in total. It contains over 21 million cells and identifies 161 cell types across 38 brain regions and 436 sub-regions, spanning 164 different developmental time points.
Users can interactively access the data in the database and compare data across species, brain regions, and developmental stages. MAPbrain also supports linked searches and comparisons of transcriptomic and epigenomic data.
Additionally, the database provides 1,078,709 gene expression sets specific to different developmental stages, helping users better understand the function and role of particular genes in developmental biology. As a continuously updated open data-sharing platform, MAPbrain offers users easy access to existing data.
To further support users, MAPbrain has developed a "CellMapping" feature that allows users to integrate their own data with the database, helping predict information such as cell types, and providing real-time feedback. This truly enables data integration and application, supporting open access and sharing of large-scale brain development data and promoting cutting-edge interdisciplinary research and translational applications.
MAPbrain looks forward to the active participation of researchers, continuously gathering more high-quality brain development research data, thereby effectively advancing the field of neurodevelopmental biology.
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae911
Contact: SONG Tingrui
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing 100101, China
E-mail: songtr@ibp.ac.cn
(Reported by Prof. WANG Xiaoqun's and HE Shunmin's group)

