Scientists Reveal Mechanism of BORC Complex Assembly in Regulating Lysosome Transport
The hetero-octameric complex BORC recruits the small G protein ARL8 to mediate the transport and localization of lysosomes. BORC-ARL8 is an essential regulatory factor in the fusion of lysosomes with autophagosomes and in targeting newly synthesized proteins to the lysosome. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the assembly of the hetero-octameric BORC complex and its interaction with ARL8 remains unclear.
On December 30, 2024, a research group led by Prof. FENG Wei at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, used a combination of biological research techniques to unveil, for the first time, the coiled-coil structure of the BORC hetero-octameric complex and identified key regions involved in the binding of BORC with ARL8. These findings provide a solid foundation for further exploration of the regulatory mechanisms underlying lysosome transport.
Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), the researchers discovered that the BORC complex is not the expected "bead-on-a-string" form but instead follows a coiled-coil assembly pattern, a structure that poses significant challenges in structural biology.
To overcome technical challenges such as severe orientation bias in cryo-EM samples and pronounced anisotropy in crystal diffraction, the researchers applied crosslinking mass spectrometry and AlphaFold structural prediction methods to successfully resolve the structure of the BORC hetero-octameric complex.
The results revealed that the eight subunits of BORC form an elongated rod-like structure. The BORC holocomplex is assembled from two hemicomplexes joined end-to-end. Each hemicomplex, consisting of four subunits (BORCS1/4/6/8 or BORCS2/3/5/7), also organizes into coiled-coil bundles.
The study also found that BORC can recruit the remaining subunits step by step through its core sub-complex of four subunits (BORCS1/2/3/5), suggesting the existence of several biologically significant sub-complexes in vivo.
Using crosslinking mass spectrometry, the researchers identified that BORC interacts with ARL8 through a peptide sequence located at the N-terminus of its BORCS5 subunit. To validate this finding, they generated a BORCS5 knockout cell line using CRISPR/Cas9 and confirmed, through rescue experiments, that this interaction plays a critical role in lysosome transport.
"Lysosomal dynamic transport is essential for the growth and invasion of cancer cells and represents a potential target for anti-cancer therapies,"Said Prof. FENG. "Our study provides important theoretical support for the biological study of lysosome transport and localization."
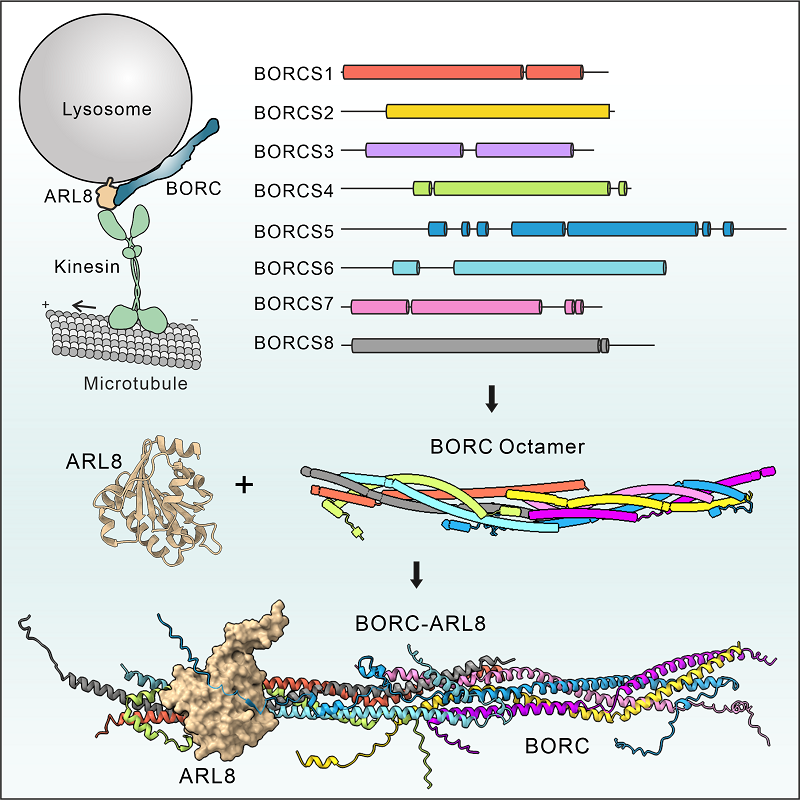
Figure. Mechanism of BORC Complex Assembly in Regulating Lysosome Transport
(Image by FENG Wei's group)
Article link: https://www.cell.com/structure/fulltext/S0969-2126(24)00536-7
Contact: FENG Wei
Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Beijing 100101, China
E-mail: wfeng@ibp.ac.cn
(Reported by Prof. FENG Wei's group)

